
Dna Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures
Biology Article Dna Structure DNA: Structure, Function and Discovery Nucleic acids are the organic materials present in all organisms in the form of DNA or RNA. These nucleic acids are formed by the combination of nitrogenous bases, sugar molecules and phosphate groups that are linked by different bonds in a series of sequences.
.jpg)
FileDNA polymerase III (with subunits).jpg Wikimedia Commons
Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated DNA) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism. DNA is made of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder — a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and.

What is the Full Form of DNA? DNA ka Full Form
Figure 13.1C. 1 13.1 C. 1: A human karyotype: This karyotype is of a male human. Notice that homologous chromosomes are the same size, and have the same centromere positions and banding patterns. A human female would have an XX chromosome pair instead of the XY pair shown.

Structure Of DNA Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures
This video explains How to Draw "DNA ; Double Helix", "ಡೀಆಕ್ಸಿರೈಬೊ ನ್ಯೂಕ್ಲೀಯಿಕ್ ಆಮ್ಲ" in easy steps in an easy.

Full form of DNA DNA ka full form kya hai DNA full form Free Learn University YouTube
In the Southern blot technique, developed by Sir Edwin Southern in 1975, DNA fragments within a sample are first separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and then transferred to a membrane through capillary action (Figure 12.16). The DNA fragments that bind to the surface of the membrane are then exposed to a specific single-stranded DNA probe.

DNA ka Full form in Hindi क्या है ? DNA TEST Full form की विस्तृत जानकारी
Deoxyribonucleic acid ( / diːˈɒksɪˌraɪboʊnjuːˌkliːɪk, - ˌkleɪ -/ ⓘ; [1] DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses.

Dna Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures
When AX molecules binds to DNA, KA and the number of binding sites (n can be represented using the logarithmic equation of Eq. . $$\mathit{log}\, ({F}_{0}-F/F)=logKA+nlog\left[DNA\right]$$. As shown in this figure, near 0.03 response unit (RU) of DNA was attached on a gold sensor surface. Due to the addition of thickness to the gold surface.

DNA Full Form Of DNA DNA Ka Full Form YouTube
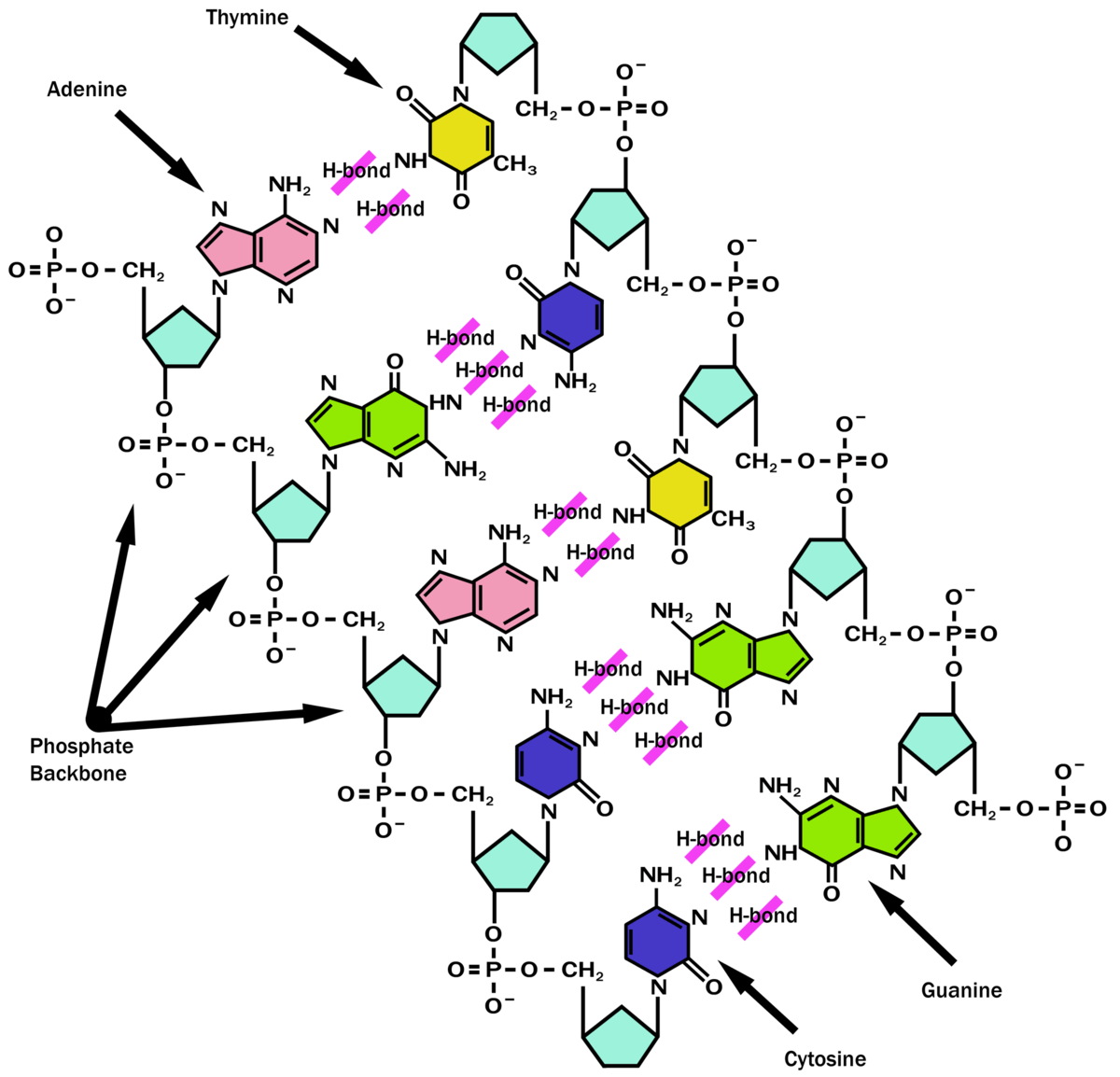
Now let's consider the structure of the two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5-carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (Figure 9.1.2 9.1. 2 ). There are four types of nitrogenous bases in.
DNA Wikipedia
The way in which the nucleotide subunits are lined together gives a DNA strand a chemical polarity. If we think of each sugar as a block with a protruding knob (the 5′ phosphate) on one side and a hole (the 3′ hydroxyl) on the other (see Figure 4-3), each completed chain, formed by interlocking knobs with holes, will have all of its subunits lined up in the same orientation.

DNA KA FIGURE DNA Ka Full Form Dioxyribose Nucleic Acid DNA shorts viral SuccessPoint777
The nucleotide is named according to the nitrogenous base it contains. Figure 9.3 (a) Each DNA nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a base. (b) Cytosine and thymine are pyrimidines. Guanine and adenine are purines.

DNA Ka Full Form और DNA Kya Hai यह जानें हिन्दी में
Nucleotides DNA and RNA are polymers (in the case of DNA, often very long polymers), and are made up of monomers known as nucleotides. When these monomers combine, the resulting chain is called a polynucleotide ( poly- = "many").

DNA Ka Full Form in Hindi डीएनए (DNA) का मतलब क्या होता है
In order for the DNA ends to pack against each other in the crystal, the DNA on the 72 bp side had to stretch by one bp localized around SHL −2 (Figure (Figure11a). 11 a). Subsequent nucleosome core particle crystal structures containing human alpha satellite DNA of variant length or sequence show stretching of one bp around SHL ± 2 and SHL.
Uncovering the Intricate 3D Architecture of Lettuce DNA A Breakthrough in DNA Functionality
Chromosome number. Different species have different numbers of chromosomes. For example, humans are diploid (2n) and have 46 chromosomes in their normal body cells. These 46 chromosomes are organized into 23 pairs: 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes. The sex cells of a human are haploid (n), containing only one homologous.

DNA ka kya use YouTube
A. DNA replication is reductive, because half the total DNA present is copied. DNA replication is semi-conservative, because each DNA strand serves as a template during replication. B. DNA replication is semi-conservative, because each DNA strand serves as a template during replication. DNA replication is dispersive, because the two resulting.

Painting Acrylic Art & Collectibles DNA
The components of DNA From the work of biochemist Phoebus Levene and others, scientists in Watson and Crick's time knew that DNA was composed of subunits called nucleotides 1 . A nucleotide is made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) or cytosine (C).

DNA क्या है ? संरचना एवं कार्य What is DNA in Hindi Structure and Functions
Go to: Abstract Quantitative measurements of biomolecule associations are central to biological understanding and are needed to build and test predictive and mechanistic models.